

Written informed consent was obtained from all subjects before the study. Ethical ApprovalĮthical approval for this study was obtained from Institutional Research Ethics Committee School of Medicine, Shahid Sadoughi University of Medical Sciences (IR.1395.205). The patients were then ensured in terms of confidentiality. The research was conducted once the permission was issued by the research council of the university, and informed consent was obtained from the participants. Concerning ethical dimension, radiography proved safe for the patients in this study. Cutoff point was determined for CTS diagnosis by length/width ratio of the wrist bones using the greatest value obtained by multiplying the sensitivity and specificity. Then, the ROC curve was drawn to calculate the area under the curve for investigating the best CTS diagnostic point by length/width ratio of the wrist bones. Sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV), negative predictive value (NPV), and accuracy of diagnosis were calculated.
Wrist xray software#
The data were analyzed using SPSS software (version 22). A single operator measured the criteria using Macropacs (Tahavolat Novin Yademan, Tehran, Iran) medical imaging software.įlowchart of patient selection. The patients were finally assigned to two groups (cases and controls). Radiography was conducted in digital imaging center of the hospital. The standard PA wrist digital radiography was performed for patients and controls. A researcher-designed checklist was deployed to collect demographic information including age and sex. Accordingly, carpal length in the axis of the 3rd ray (the distance between the proximal of lunate bone to the third metacarpal base), carpal width (the shortest distance between the medial part of trapezium tubercle to the most lateral part of hamate hook), and carpal ratio (calculated by dividing carpal length to carpal width) were considered as the radiographic criteria, respectively (Figure 1). The hypothesis outlined here was based on the relationship between carpal tunnel length/width ratio and the likelihood of severe CTS. The participants in the control group were selected from among adult volunteers without CTS risk factors and those with no history of CTS.Ī single assessor took a careful history and examined the cases. The subjects were selected out of the outpatients affected with upper extremity symptoms visiting the subspecialty polyclinic of the area affiliated to a general hospital from January 2019 to January 2020.Ĭases with a history of metabolic or rheumatologic diseases, trauma, or any operation in the wrist as well as the mild and moderate cases of CTS were excluded. The sample size was calculated according to the CTS estimated prevalence in our society population. In this case-control study, we included all severe cases of CTS predicated on physical examinations and electrodiagnostic findings. We attempted to conduct a case-control study to determine whether the measurement of carpal bone dimensions by a digital X-ray can predict severe CTS in case the results proved positive, the technique could be used for the screening patients suspected of CTS along with the physical exam findings.
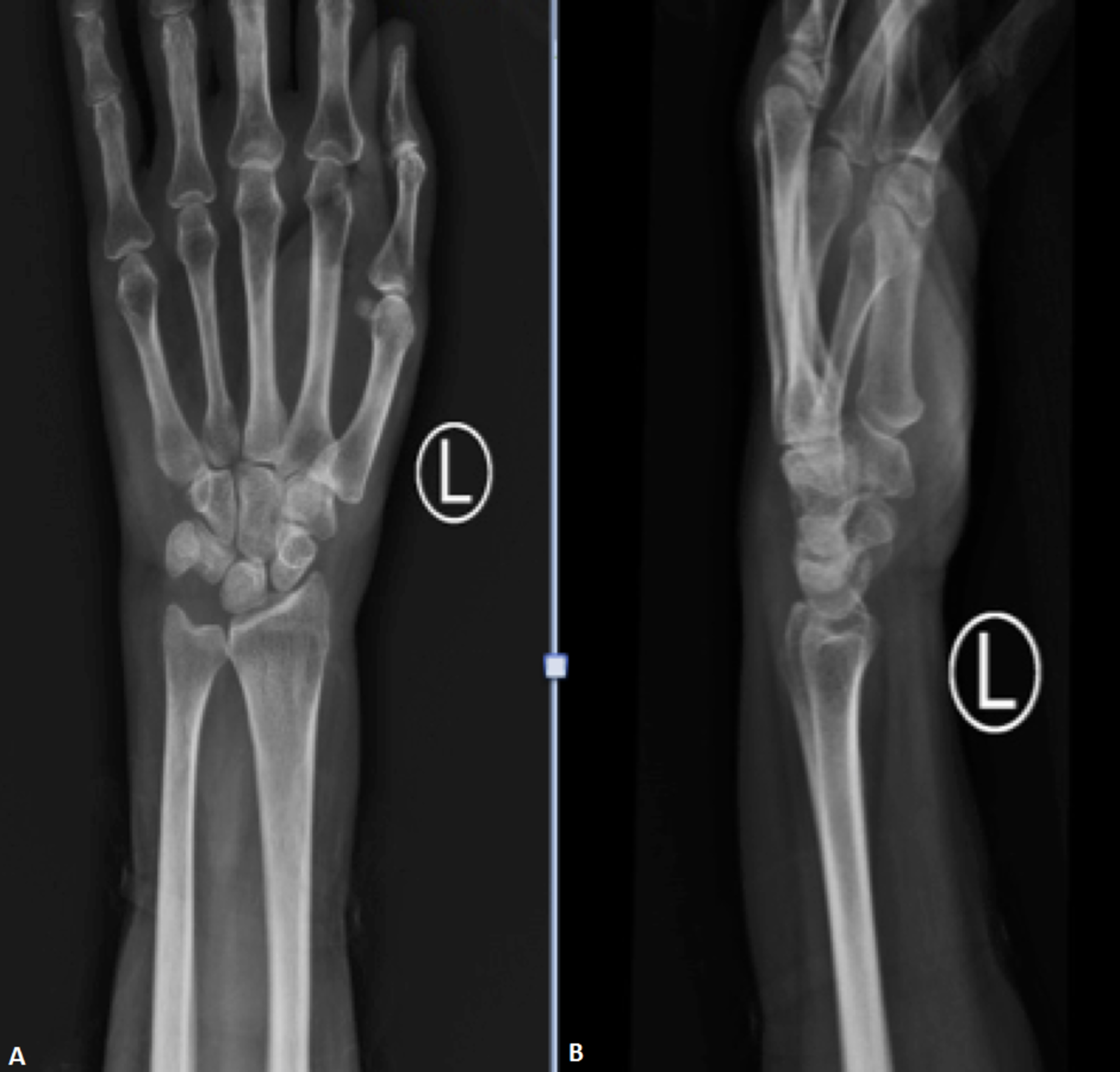
Recently, digital X-ray machines have proven popular and medical imaging softwares can measure decimal distances in digital images. Moreover, MRI and anthropometric measurements are used for diagnosis and prediction of the treatment however, they cannot be replaced for EDS as a gold standard diagnostic test. There are controversial results concerning the usefulness of ultrasound findings for evaluation of CTS. Because electrodiagnostic studies are invasive procedures, other diagnostic modalities such as sonography are used for the purpose.

CTS diagnosis is based on the clinical signs and symptoms and is confirmed by electrodiagnostic studies. IntroductionĬarpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is the most common entrapment neuropathy in extremities, which is caused by the compression of the median nerve in the wrist. According to the ROC chart, the cutoff points, positive and negative predictive values, and the diagnostic accuracy for the cutoff points were calculated. In this study, 119 participants, including 50 patients and 69 healthy subjects, were recruited. In the posteroanterior view of the wrist plain radiography in both groups, we defined and measured the carpal ratio, and the results were analyzed deploying statistical software. This is a case-control diagnostic probe in which patients with severe CTS documented by electrodiagnostic study and healthy subjects as controls were enrolled. In this study, we evaluated the diagnostic value of carpal dimensions in wrist plain radiography for the screening of carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
